The onset of menopause marks a significant transition in a woman’s life, bringing with it a unique set of physical, emotional, and cognitive changes. Understanding the first signs of menopause is crucial for women to navigate this journey with knowledge and confidence.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse aspects of menopause, empowering women with essential information on its symptoms, long-term implications, and available support systems. By shedding light on the initial indicators of this natural process, we aim to equip women with the tools they need to embrace this phase with grace and understanding.
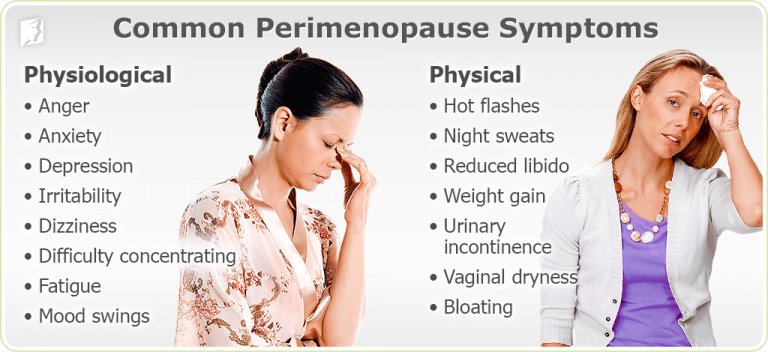
Physical Signs of Menopause

Menopause, the natural cessation of menstruation, is accompanied by a range of physical signs that manifest due to hormonal changes. Understanding these physical manifestations is crucial for women experiencing menopause.
The decline in estrogen and progesterone levels during menopause triggers various physiological alterations, leading to the following physical signs:
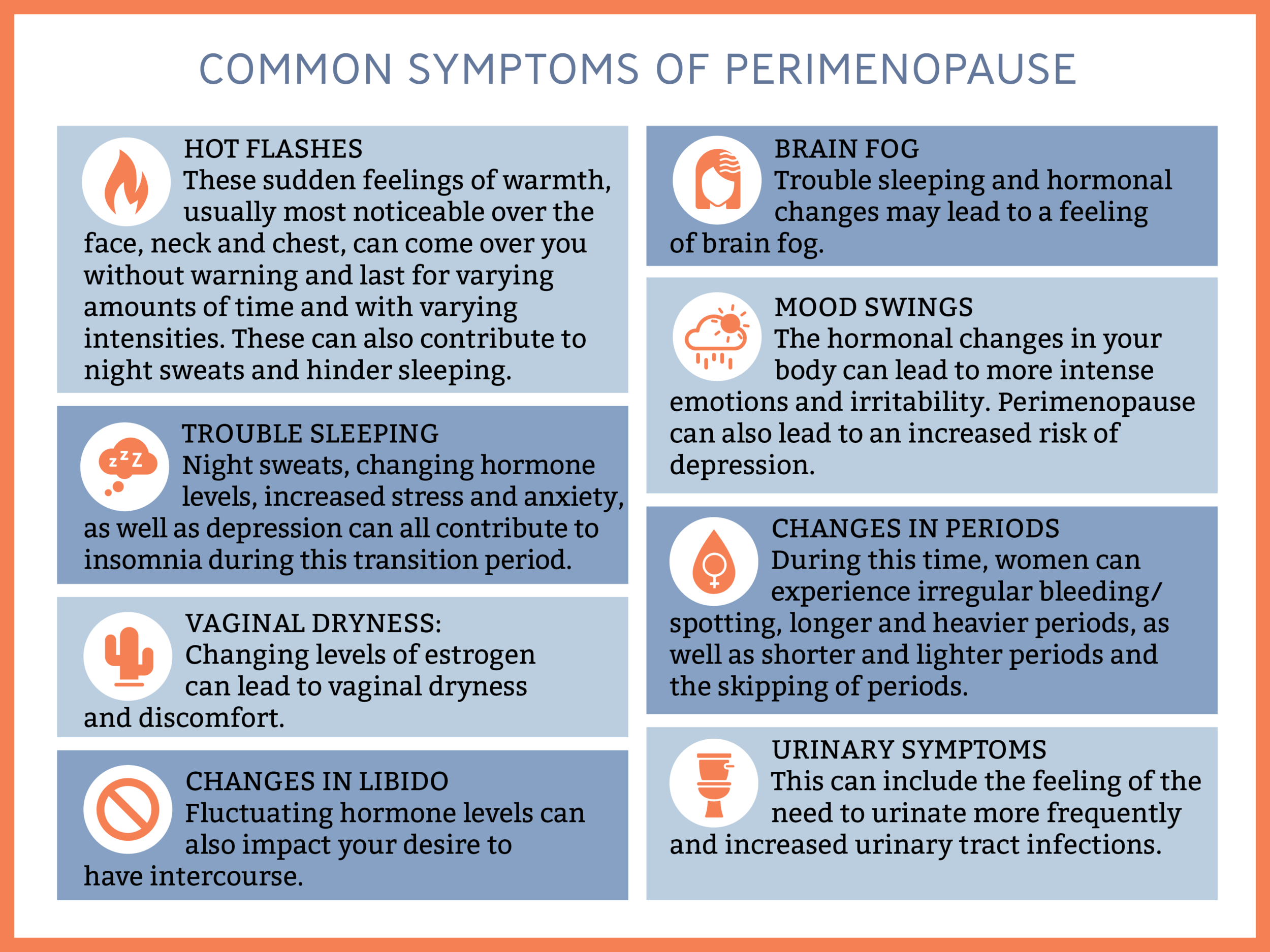
Hot Flashes and Night Sweats
- Sudden episodes of intense heat and sweating, especially in the face, neck, and chest.
- Caused by the body’s attempts to regulate temperature due to decreased estrogen levels.
Vaginal Dryness
- Thinning and drying of the vaginal walls.
- Caused by reduced estrogen levels, leading to decreased blood flow and lubrication.
Sleep Disturbances
- Difficulty falling or staying asleep, frequent awakenings.
- Hot flashes, night sweats, and hormonal changes can disrupt sleep patterns.
Mood Changes
- Irritability, anxiety, mood swings, and depression.
- Hormonal fluctuations, particularly decreased estrogen, can affect brain chemistry.
Osteoporosis
- Loss of bone density, increasing the risk of fractures.
- Estrogen deficiency impairs the body’s ability to absorb calcium and maintain bone mass.
Weight Gain
- Increased body fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Hormonal changes, decreased metabolism, and reduced physical activity can contribute to weight gain.
Skin Changes
- Dry, thinning skin, loss of elasticity.
- Decreased collagen production due to reduced estrogen levels.
Hair Changes
- Thinning hair, hair loss.
- Hormonal changes and reduced blood flow to hair follicles.
Emotional and Cognitive Symptoms
Menopause, a natural transition in a woman’s life, often brings about a range of emotional and cognitive changes. These symptoms arise due to the fluctuating levels of hormones, primarily estrogen and progesterone, which play crucial roles in regulating mood, memory, and other cognitive functions.
Emotional Symptoms, First signs of menopause
The hormonal shifts during menopause can lead to a spectrum of emotional symptoms, including:
- Irritability and mood swings
- Anxiety and depression
- Increased emotional sensitivity
- Reduced libido
- Difficulty concentrating and making decisions
Cognitive Symptoms
Menopause can also affect cognitive abilities, resulting in symptoms such as:
- Memory lapses and difficulty recalling information
- Reduced attention span and difficulty focusing
- Impaired spatial reasoning and problem-solving abilities
- Changes in sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and reduced alertness
Understanding these emotional and cognitive symptoms is essential for women experiencing menopause. Recognizing and addressing these changes can help alleviate discomfort and promote well-being during this transitional phase.
Long-Term Health Implications
Menopause can have long-term implications for women’s health. Understanding these risks and implementing preventive measures is crucial for maintaining well-being during and after this transition.
Osteoporosis
Estrogen plays a vital role in maintaining bone density. As estrogen levels decline during menopause, women become more susceptible to osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened and brittle bones.
- Increased risk of fractures, particularly in the hip, spine, and wrist.
- Regular weight-bearing exercise, adequate calcium intake, and vitamin D supplementation can help preserve bone health.
Cardiovascular Disease
Estrogen also exerts a protective effect on the heart and blood vessels. After menopause, women’s risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke, increases.
- Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels can reduce the risk.
- Hormone therapy may be considered for some women to mitigate these risks.
Cognitive Decline
Some studies have suggested a link between menopause and an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia. However, the exact nature of this relationship is still being investigated.
- Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, such as reading, puzzles, and social interactions, can help maintain cognitive function.
- Adequate sleep, stress management, and a healthy diet may also play a role in preserving cognitive health.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Factors
Menopause can be influenced by modifiable lifestyle and behavioral factors. These include:
-
-*Diet
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the severity of menopausal symptoms.
-*Exercise
Regular exercise can help improve mood, reduce stress, and alleviate hot flashes and night sweats.
-*Stress reduction techniques
Stress can worsen menopausal symptoms. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
Diet
Eating a balanced diet can provide essential nutrients that support hormone balance and overall health. Some specific recommendations include:
-
-*Fruits and vegetables
Aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables daily. They are rich in antioxidants and phytoestrogens, which may help reduce hot flashes and other symptoms.
-*Whole grains
Whole grains are a good source of fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of weight gain.
-*Lean protein
Lean protein sources, such as fish, poultry, and beans, can help maintain muscle mass and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
-*Calcium and vitamin D
Calcium and vitamin D are essential for bone health. Aim for 1,000 mg of calcium and 600 IU of vitamin D daily.
Exercise
Regular exercise can improve physical and mental health during menopause. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
-
-*Aerobic exercise
Aerobic activities, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can help improve cardiovascular health and reduce stress.
-*Strength training
Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, can help maintain muscle mass and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
-*Yoga and Pilates
Yoga and Pilates are mind-body exercises that can help improve flexibility, balance, and reduce stress.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress can exacerbate menopausal symptoms. Techniques that can help manage stress include:
-
-*Yoga and meditation
Yoga and meditation can help reduce stress, improve mood, and promote relaxation.
-*Deep breathing
Deep breathing exercises can help calm the nervous system and reduce stress.
-*Massage
Massage can help relax muscles, reduce tension, and improve overall well-being.
-*Spending time in nature
Spending time in nature has been shown to reduce stress and improve mood.
Medical Interventions
Menopause is a natural process, but it can lead to a range of symptoms that can affect a woman’s quality of life. Medical interventions can help manage these symptoms and improve overall well-being.
There are a variety of medical interventions available to manage menopausal symptoms, including:
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT is a treatment that replaces the hormones that are lost during menopause. It can help relieve hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and other symptoms. HRT can be taken in a variety of forms, including pills, patches, and gels.
HRT is effective in managing menopausal symptoms, but it can also have some risks, including an increased risk of blood clots, heart disease, and breast cancer. It is important to talk to a doctor about the risks and benefits of HRT before starting treatment.
Antidepressants
Antidepressants can be helpful in managing some of the emotional symptoms of menopause, such as anxiety, depression, and mood swings. Antidepressants work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin and norepinephrine.
Antidepressants can be effective in managing menopausal symptoms, but they can also have some side effects, such as nausea, dizziness, and dry mouth. It is important to talk to a doctor about the risks and benefits of antidepressants before starting treatment.
Other Medications
There are a number of other medications that can be used to manage menopausal symptoms, including:
- Gabapentin for hot flashes
- Clonidine for hot flashes
- Vaginal estrogen for vaginal dryness
- Ospemifene for vaginal dryness
- Prasterone for sexual dysfunction
It is important to talk to a doctor about the risks and benefits of any medication before starting treatment.
Cultural and Societal Perspectives: First Signs Of Menopause
Menopause is a significant transition in a woman’s life, and the cultural and societal perceptions surrounding it can greatly impact her experience. These perceptions vary widely across different regions and demographics, influencing women’s attitudes, coping mechanisms, and access to support.
In some cultures, menopause is seen as a natural and respected stage of life, associated with wisdom and maturity. Women may be celebrated for their experience and knowledge, and their role in society may shift to one of elder or matriarch.
In contrast, other cultures may view menopause as a decline or a loss, leading to stigma and discrimination.
Impact on Women’s Experiences
Cultural perceptions can profoundly affect women’s well-being during menopause. In cultures that stigmatize menopause, women may experience shame, isolation, and a sense of devaluation. They may be less likely to seek medical help or support, leading to poorer health outcomes.
Conversely, in cultures that embrace menopause, women may feel more confident and empowered. They may have access to traditional remedies, support networks, and rituals that help them navigate this transition. This can lead to a more positive and fulfilling experience.
Support and Resources
Navigating menopause can be a challenging and isolating experience. However, various support groups, online communities, and professional resources are available to provide guidance, emotional support, and practical advice.
Emotional support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals can play a crucial role in managing the emotional and psychological aspects of menopause. Joining support groups or connecting with others going through similar experiences can foster a sense of community and understanding.
Professional Guidance
Seeking professional guidance from healthcare providers, such as gynecologists or mental health professionals, is essential for addressing physical and emotional concerns during menopause. They can provide personalized medical advice, prescribe medications if necessary, and offer support and counseling to help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Support Groups
Support groups specifically tailored for women experiencing menopause provide a safe and confidential space to share experiences, offer encouragement, and learn from others. These groups may be organized through local hospitals, community centers, or online platforms.
Online Communities
Numerous online communities and forums exist where women can connect with others going through menopause. These platforms offer a convenient way to access support, share information, and participate in discussions from the comfort of their own homes.
FAQ Corner
What are the most common physical signs of menopause?
Hot flashes, night sweats, irregular periods, vaginal dryness, and sleep disturbances are some of the most prevalent physical signs.
How can I manage emotional and cognitive changes during menopause?
Exercise, stress-reducing techniques, and seeking support from family, friends, or a therapist can help alleviate emotional and cognitive symptoms.
What are the potential long-term health risks associated with menopause?
Osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and cognitive decline are potential long-term health concerns that women should be aware of and take steps to manage.